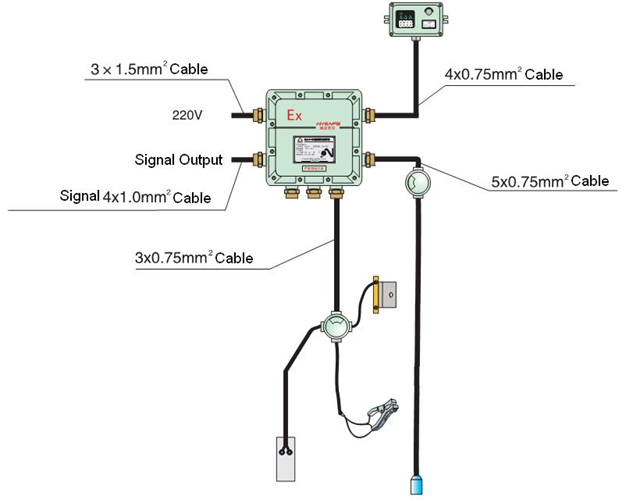
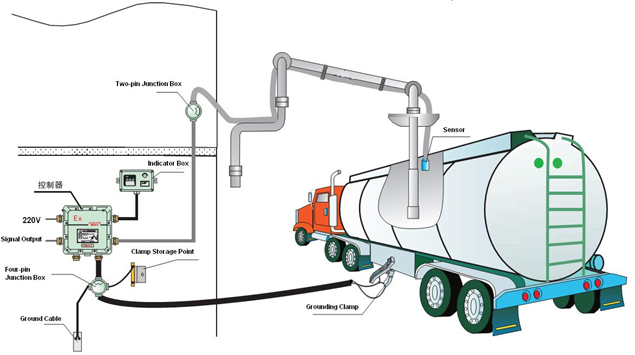
Grounding and overfill protection are critical safety features implemented in loading gantries in oil and gas fields to prevent accidents and environmental hazards during the transfer of petroleum products. Here’s what each term refers to:
- Grounding: Grounding, also known as earthing, is the process of connecting the metal components of the loading gantry to the earth or ground. This is done to prevent the buildup of static electricity, which can occur during the transfer of flammable liquids like oil and gas. Static electricity can create sparks, which could potentially ignite the flammable vapors, leading to fires or explosions.Grounding systems typically consist of metal rods or cables that are securely connected to the gantry structure and then buried in the ground. By providing a path for the discharge of static electricity, grounding helps to dissipate any charges that may accumulate, thereby reducing the risk of ignition.
- Overfill Protection: Overfill protection systems are designed to prevent tanks or vessels from being overfilled during the loading process. When transferring liquids such as oil or gas, it’s essential to ensure that the containers receiving the product do not exceed their maximum capacity, as overfilling can lead to spills, leaks, or even catastrophic failures.Overfill protection systems typically include sensors or probes installed in the tank or vessel, which can detect when the liquid level reaches a predetermined threshold. Once this threshold is reached, the system triggers an alarm to alert operators to stop the flow of product. In some cases, overfill protection systems may also automatically shut off the flow of product to prevent overfilling from occurring.
By incorporating grounding and overfill protection systems into loading gantries, oil and gas companies can minimize the risk of accidents, protect the environment, and ensure compliance with safety regulations.